Vegan Mozzarella: Dairy-Free Production Methods & Melting Properties

Vegan mozzarella relies on three key components: starch polymers (like oxidized potato starch), plant proteins, and oil emulsions. You'll need oxidized potato starch that melts above 70°C as your foundation, combined with properly denatured proteins from nuts, soy, or peas. Oil-in-water emulsions are instrumental for controlling melting behavior, preventing protein aggregation, and mimicking dairy cheese's stretch.
Balancing these elements precisely creates vegan cheese that flows at temperatures similar to conventional mozzarella. The science behind these plant-based interactions reveals fascinating culinary possibilities.
The Science Behind Plant-Based Protein Networks
Building effective plant-based alternatives to dairy mozzarella requires understanding the fundamental architecture of protein networks. These networks form the structural foundation that gives vegan cheese its characteristic stretch and bite.
When you create plant-based cheese, you're fundamentally engineering protein interactions that mimic dairy casein. Plant proteins from nuts, soy, or peas must be properly denatured and cross-linked to form cohesive matrices. Coconut oil contributes essential fatty components that provide creaminess and mouthfeel, while tapioca starch acts as a binding agent that improves melting properties.
The success of your vegan mozzarella depends on how these protein networks respond to heat. Unlike dairy proteins, plant proteins require specific pH conditions and stabilizers to achieve comparable stretchability. By manipulating these elements, you'll create a plant-based cheese that melts and stretches convincingly.
The aging process plays a crucial role in developing complex flavors and ensuring proper protein network formation in vegan mozzarella.
Role of Starch Polymers in Vegan Cheese Structure
Three critical polymer interactions define the structural integrity of vegan mozzarella. When you create vegan cheese, starch polymers form the foundational gel matrix that mimics dairy cheese's texture.
Adding protein networks to this starch base considerably reduces melting, making your cheese hold its shape better when heated.
You'll notice that protein alone creates visible aggregation in starch gels, resulting in a coarse appearance. However, incorporating emulsion droplets prevents these large protein aggregates from forming, improving the cheese's visual appeal.
The most effective approach you can take combines both protein networks and emulsion systems within the starch polymer structure. This combination offers superior control over melting properties while maintaining an appealing texture—an essential balance when developing vegan mozzarella that both looks and behaves like its dairy counterpart.
Emulsion Stabilization Techniques for Improved Meltability
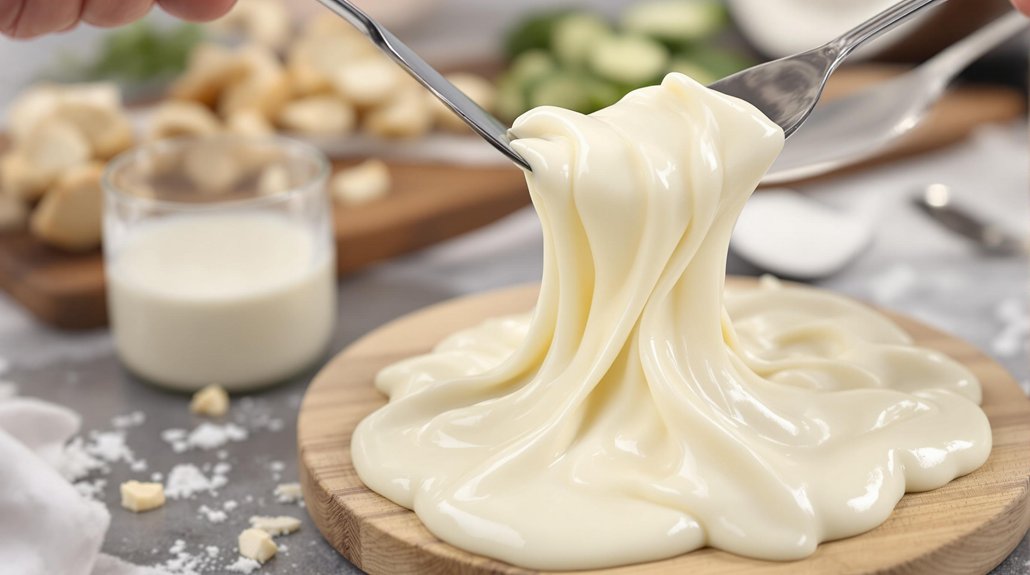

When developing vegan mozzarella, the right emulsion stabilization technique can noticeably improve your cheese's meltability. Incorporating oil-in-water emulsions into your starch-based formulations prevents excessive flow while maintaining desirable stretch.
Protein-stabilized emulsions outperform low-molecular-weight emulsifiers when controlling melting properties of starch gels. These emulsion droplets serve a dual purpose—they limit melting during heating while preventing the formation of visible protein aggregates that create a coarse texture.
You'll need to carefully balance starch, protein, and oil content in your formulation. This balance is critical for achieving the signature stretch and pull of traditional mozzarella without compromising structural integrity. By implementing emulsion-based approaches, you'll create vegan cheese with markedly better melting functionality than starch-only systems.
Temperature Thresholds: When Vegan Mozzarella Begins to Flow
Understanding exact temperature thresholds marks the difference between vegan mozzarella that gracefully melts and one that collapses into an oily puddle. Research shows oxidized potato starch gels completely melt above 70°C, making them ideal foundations for melty vegan cheese, while native maize starch remains stubbornly solid.
You'll find the best results when incorporating protein-stabilized sunflower oil emulsions into your starch gels. These create networks that control melting behavior at essential temperature thresholds.
However, balance is pivotal—too much protein aggregation creates unappealing, inhomogeneous textures, while too little leads to syneresis (liquid separation).
For perfect vegan mozzarella, aim for that sweet spot where proteins and oils form a structure that mimics dairy cheese's melt profile without collapsing. Temperature sweep tests confirm these composites can be precisely engineered to flow at temperatures resembling conventional mozzarella.
Enhancing Stretch: Tapioca Starch and Alternative Thickeners
Achieving that perfect stretchy pull of melted mozzarella represents one of the greatest challenges in vegan cheese-making. Without casein and sufficient saturated fat, plant-based alternatives need specific thickeners to replicate authentic melting properties.
Tapioca starch stands out as your primary solution for creating stretchy texture in vegan mozzarella. You'll find that replacing corn starch with tapioca at a ratio of 5 tablespoons to 2 tablespoons dramatically improves both stretch and melt. This substitution addresses the fundamental structural differences between plant and dairy proteins.
For additional options, consider kappa carrageenan, which provides similar consistency benefits. You can also fine-tune your recipe by adjusting the tofu-to-milk ratio from 60ml to 50 grams, enhancing stretching capacity. These modifications compensate for vegan cheese's inherent compositional limitations while maximizing its potential for that coveted mozzarella-like pull.
Commercial vs. Homemade Vegan Mozzarella Melting Comparison
The expectation gap between commercial and homemade vegan mozzarella often leaves cheese enthusiasts disappointed when they attempt their first pizza. While commercial brands like Violife and Daiya offer convenient options with varying melting properties, your homemade version might behave differently—more like chocolate than dairy cheese.
For better melting results:
- Heat management - Commercial vegan cheese typically requires higher temperatures, while homemade mozzarella needs gentle, gradual heating with constant stirring
- Ingredient balance - Homemade recipes with silken tofu, tapioca starch, and nutritional yeast create better melting properties than commercial options lacking these elements
- Texture expectations - Adjust your expectations; even well-made vegan cheese maintains some structure while becoming smearable rather than liquefying completely
The vegan cheese industry continues improving melting capabilities, narrowing the gap between plant-based and dairy mozzarella.
Oil Content Impact on Thermal Behavior and Mouthfeel
Oil content creates a paradoxical relationship in vegan mozzarella, simultaneously enhancing creaminess while potentially compromising meltability. When you increase oil concentrations, you'll notice improved mouthfeel and perceived creaminess, but this comes at the cost of reduced thermal flow properties that affect how the cheese spreads when heated.
The interaction between the protein network and oil droplets is critical for achieving ideal melting properties. As you experiment with different oil types like coconut or sunflower, you'll see varying rheological behaviors in your vegan cheese. The key challenge lies in finding the perfect balance - enough oil to deliver the rich, creamy texture consumers expect, but not so much that it prevents the proper melting behavior necessary for applications like pizza or grilled cheese sandwiches.
Protein Aggregation: Challenge or Opportunity for Texture
Protein aggregation represents a double-edged sword in vegan mozzarella development, posing both challenges and opportunities for texture control. When you're formulating plant-based cheese, you'll need to carefully balance protein content to avoid both syneresis (when protein is too low) and an inhomogeneous appearance (when aggregation is excessive).
A protein network outperforms an emulsion network when you're aiming to control melting properties - a vital factor for authentic mozzarella performance on pizza.
Use emulsion droplets strategically to prevent formation of visible protein aggregates.
Adjust protein content to avoid syneresis while maintaining desired texture.
Incorporate controlled protein aggregation to achieve ideal melting characteristics.
Strategies to Prevent Syneresis in Melted Vegan Cheese
While developing the perfect vegan mozzarella, you'll find that preventing syneresis during melting represents one of the most critical challenges.
Incorporating heated pea protein networks into your starch-based formulations creates structural stability that effectively limits unwanted moisture release.
You'll achieve superior results by creating protein-stabilized emulsions with sunflower oil, which greatly improves melting characteristics while minimizing syneresis in your starch gels. These emulsion droplets serve a dual purpose, preventing the formation of large protein aggregates that could otherwise create an uneven appearance in your final product.
For the best performance, you'll need to carefully balance protein and oil content in your formulations. This strategic combination of starch, protein, and oil delivers the ideal solution for creating vegan cheese that melts beautifully without releasing water.